Fastener Realization Methods
Overview of the fastener connector realization process and methods.
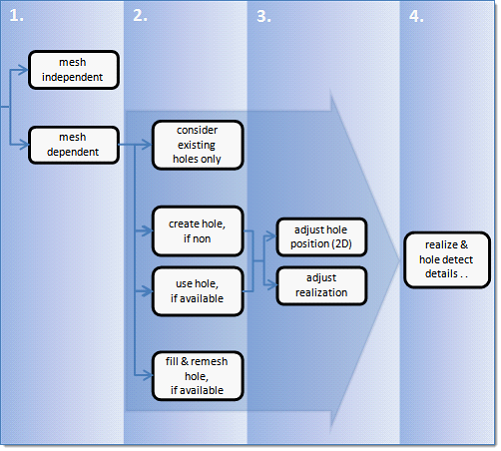
Figure 1.
Depending on the realization type, the mesh connectivity will automatically be assigned as independent or dependent.
- mesh independent
- Use for realizations which do not need any mesh changes, and the connection is primarily defined via a solver-specific card or the nodes which need to be connected are defined by a cylinder, such as Bolt (cylinder spring) for Radioss.
- For all mesh independent fastener realization types, a cylinder is defined. Fastener hole detection is not performed because holes are not required. All of the nodes inside the cylinder are considered part of the fastener realization unless they also belong to a link defined on the connector.
- The cylinder dimension is primarily defined by its diameter, length L1
and L2.
- L1 points in the same direction as the connector vector and describes the distance from the connector position to the first end of the cylinder.
- L2 points in the opposite direction and measures the distance between the connector position and the second end of the cylinder.
- Therefore, the connector vector is essential for these types of realizations.
- If a vector is not predefined and is determined dynamically, the vector
will always point from the connector position to the projection point on
the farthest link.
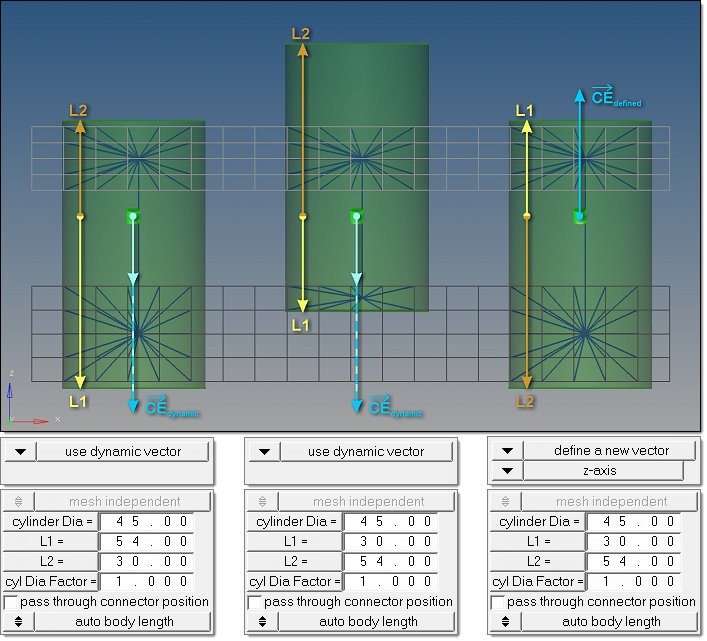
Figure 2. . Dynamic vectors have been used in the first two cylinder. Interchanging the values for L1 and L2 leads to very different realizations. By comparison, the third cylinder uses the same values for L1 and L2 as in the second cylinder, but the result looks better because of the predefined connector vector in the global z-direction. - In some automated processes, the cylinder diameter is automatically set
to the fastener shaft diameter. This leads to failed cylinder fasteners
when the holes are properly modeled because the defined cylinder does
not contain nodes. In such cases, the cylinder diameter factor has been
introduced; this factor is set to 1.0 by default and is a multiplier for
the cylinder diameter to increase the final cylinder diameter when
necessary. Note: The cylinder diameter as well as the cylinder diameter factor can be reviewed and modified in the Connector Browser. Connectors can also be rerealized with modified cylinder diameters and cylinder diameter factors without updating L1 or L2 in the browser. This is not possible from the panel.
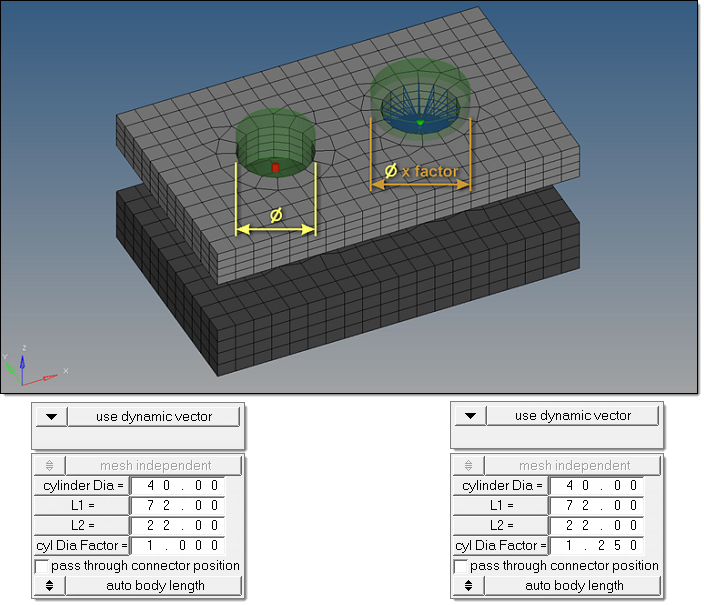
Figure 3. - mesh dependent
- Use for all other cases.
-
For mesh dependent types, you must determine:
- Is the existence of holes in each layer requested upfront?
- How should the 2D mesh be prepared before the final realization is performed?
In the past, a fastener realization always required a hole for each layer in the initial mesh. This is no longer necessary for 2D meshes because the imprint capability punches the needed holes into the mesh before the final realization is performed, enabling the mesh to be manipulated in a pre-step. This makes it possible to punch holes, move holes, close holes, create washers, and so on.
Under the Connectivity heading, select one of the following:- consider existing hole only
- A minimum of one hole per layer must be available in the origin
mesh. If holes do not exist, the realization will fail. This is
the default method and must be used for any type of solid
meshes.
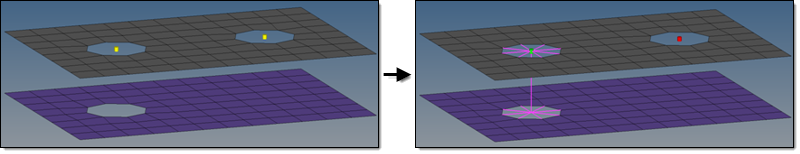
Figure 4. - create hole, if none
- If there are not any holes on a certain layer, they will be
punched into that layer at the position of the projection point.
The diameter of the new hole is defined under the Realization
Details heading. This method is used if the model does not
contain the appropriate amount of holes per fastener, but holes
are required for specific realization types.
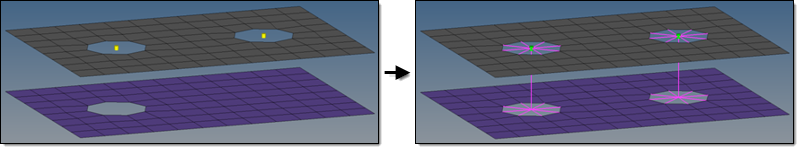
Figure 5. - use hole, if available
- Creates hybrids (hole on one side only), but other combinations
are allowed. On the mesh side (no hole), the connection is
realized via the head elements defined in the chosen realization
type. The head element(s) is/are created between the appropriate
body element node and the nodes inside the diameter
(no hole connection dia) defined
under the Realization Details heading. This option is used for
realization types which are not eager for holes.
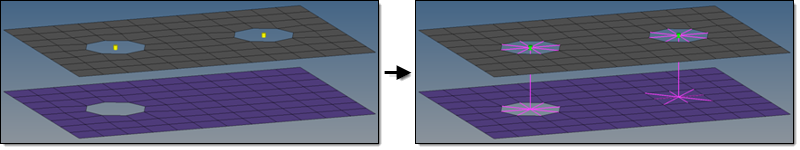
Figure 6. - fill & remesh hole, if available
- Use this option when you do not want the shape of holes to
interfere with the mesh flow in the fastener region. The
detected holes are closed and a remesh of the new elements and a
few additional rows of adjacent elements is performed. The
connection is realized via the head elements defined in the
chosen realization type. The head elements are created between
the appropriate body element nodes and the nodes inside the
diameter (no hole connection dia) defined
under the Realization Details heading.
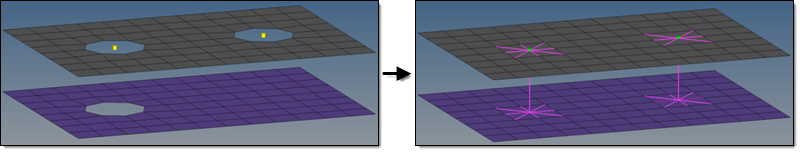
Figure 7.
Note: The hole detection mechanism for the last three options takes into account a cylinder which is defined under the Realization Details heading. The hole consideration cylinder option can be defined as a factor of the no hole connection dia option or as an exact diameter. Principally holes which are inside or touching the cylinder can be detected, but the hole consideration is reduced to one hole per link per connector. Additionally, holes need to fit to the requested dimensions, which are also defined under the Realization Details heading. -
For the create hole, if none, and use
hole options, a mesh modification including a hole movement is
allowed. Therefore, you can determine whether to adjust the hole(s) or to adjust
the realization.
- adjust hole position (2D)
- Moves the center of a hole into the position of the projection
point.
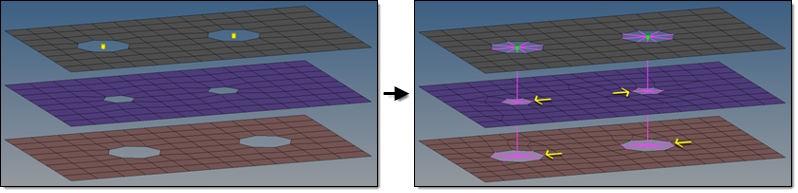
Figure 8. - adjust realization
- Hole positions are not modified, enabling the realized elements to
compensate the nonaligned centers of holes.
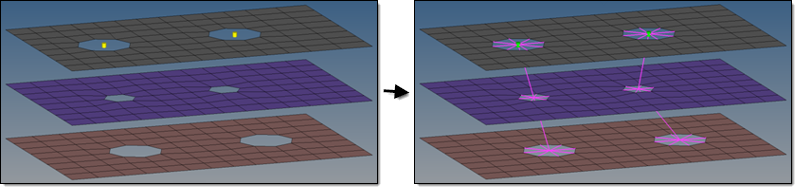
Figure 9.
-
Define behavior options.
- After Imprint
- During realization, if the mesh is altered to realize the connector, this option allows you to select between "Remesh" and "Rebuild" meshing algorithms.
- Rebuild Washer
- Perform a rebuild operation on the created washer in cases where the washer is very close to a feature edge. This will potentially change the shape of the washer to snap to feature edges to avoid poor mesh quality.
- Unrealize Fill Hole Created
- If the control is set to Create hole, if none, this fills the created hole when the connector is unrealized, returning the surface back to its original configuration before realization
-
Define realize and hole detection details
This stage cannot be skipped, as it has great influence on stages 2 and 3, which is expressed by the large arrow underlying those stages in the flow chart.
This stage contains all realize and hole detection details which need to be known before the final realization is done. The realize and hole detection are found under the Realization Details heading.
- Hole Detection Details
-
- Dimension and Feature Angle
- The minimum and maximum dimensions define which holes should be considered during fastener realization. The minimum and maximum feature angle define the features to be considered as hole edges for solid elements.
- Hole Consideration Cylinder
- Not all of the holes found in the given connector
tolerance can be considered for the various fastener
realizations.
- The connector tolerance, especially when set to a large value, detects many holes. To prevent detecting holes which are far away from the connector position and are not aligned with the other hole(s), the consideration cylinder excludes outer holes from the detection.
- Since the existence of a hole is not
necessarily requested anymore, a space has to be
defined where the holes are expected to be. It is
no longer sufficient to use just the connector
tolerance, therefore the Hole
Consideration Cylinder option
performed along the projection path becomes
necessary. All of the holes the cylinder touches
or contains can be considered for the various
fastener realizations.
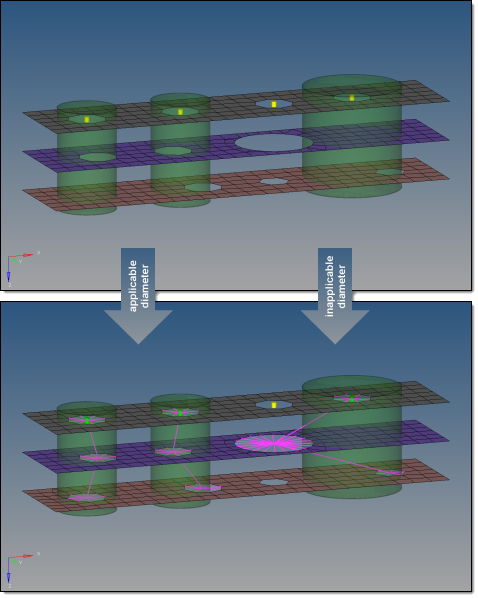
Figure 10.
- Define cylinder diameters in the following ways:
- auto cylinder diameter (factor)
- Factors given diameters, which include: create hole diameter (2D), create/adjust hole diameter (2D), adjust hole diameter (2D), and no hole connection diameter. The first available diameter is used. The default factor is 1.5.
- exact cylinder diameter
- Specify an exact diameter. The default
diameter is 15.0Note: The hole consideration cylinder option is not offered when using the consider existing holes only option.
- Realization Details
- Depending on the options selected in stage 2, varying subsets of the options are offered.
- Diameter and adjustments options include:
- create hole diameter (2D)
- Create new holes with the specified diameter. Used
if holes are required by the create hole,
if none option.

Figure 11. - create and adjust hole diameter (2D)
- Create new holes with the specified diameter and
adjust existing holes with the specified diameter,
which leads to fastener realizations with the exact
same diameter on all links. Used if holes are
required by the create hole, if
none option.

Figure 12. - adjust hole diameter (2D)
- Adjust existing holes to the specified diameter. The
do not adjust hole diameter
option switches off the adjustment and uses the
holes with their origin size. Used if holes are not
necessarily required when using the use
hole, if available option, but the
existing holes need to have a specific diameter.

Figure 13. - no hole connection diameter
- Connect a link without an available hole by joining the nodes found inside the circle with the specified diameter around the projection point via head elements. Used if holes are not required when using the use hole, if available option or fill and remesh hole, if available option.
- Hole filling and number of nodes around holes options include:
- Fill Holes (2D)
- Fill detected holes during fastener realization.
There are various quad patterns available, which
cause a remeshing of the area around the hole.
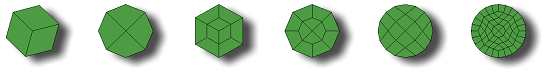
Figure 14. - Holes can also be filled with pie pieces. If the
number of pie pieces is defined, the surrounding
mesh is remeshed. The pie pieces
preserve option also creates pie
pieces, but takes the existing hole nodes into
account and prevents the remeshing.Note: Activating the fill holes (2D) option deactivates the no. of nodes around hole option.

Figure 15. - Nodes around Hole
-
- preserve
- Use the number of nodes of the appropriate origin hole. This is the default option which prevents the surrounding mesh from being remeshed. For new holes, the auto option is used.
- density
- Specify the exact number of nodes (default is 8). The surrounding mesh gets remeshed.
- elem size
- Specify an element size (default is 5.0). The number of elements around the hole is calculated based on this size. This is the preferred option for extremely different hole diameters. The surrounding mesh gets remeshed.
- auto
- Perform a node distribution based on the underlying mesh size. The number of nodes is always rounded to an equal number.
- Create washer layer options:
For 2D holes, one or two washer layers can be created, after which the surrounding mesh gets remeshed.
The width of the washer can be defined by:- Factoring the hole radius.
- Directly specifying the exact width.

Figure 16.