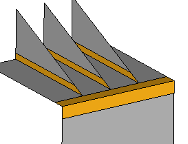
Cross Extend Surfaces
Use the Surfaces: Cross Extend tool to extend surfaces to meet each other, or other target surfaces.
View new features for HyperWorks 2022.
Learn the basics and discover the workspace.
Discover HyperWorks functionality with interactive tutorials.
Start HyperWorks and configure the applications.
Create, open, import, and save models.
Set up sessions and create report templates.
Solver interfaces supported in HyperWorks.
A solver interface is made up of a template and a FE-input reader.
Create and edit 2D parametric sketch geometry.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
Explore the tools used to create geometry.
Learn about creating, editing, and extracting points and nodes.
Create and edit circles and rectangles with the Shapes tool.
A line represents a curve in space and is not attached to any surface or solid. A line is a one-dimensional geometric entity.
A surface represents the geometry associated with a physical part. A surface is a two-dimensional geometric entity that may be used in automatic mesh generation.
Use the Surfaces: Patch tool to create patch surfaces between free lines that are not connected or surface edges. You can also delete surfaces with this tool.
Use the Surfaces: Extend tool to create tangent or normal extension surfaces.
Use the Surfaces: Cross Extend tool to extend surfaces to meet each other, or other target surfaces.
Use the Surfaces: Offset tool to offset surfaces or solids in a normal direction.
Solids are closed volume of surfaces that can take any shape. Solids are three-dimensional entities that can be used in automatic tetra and solid meshing.
Use the Ruled tools to create surfaces/solids by interpolating lines and surfaces either linearly or smoothly.
A face is a single Non-uniform Rational B-Spline (NURBS) and is the smallest area entity. It has a separate underlying mathematical definition, specified when it was created.
Use the Drag/Spin tool to drag and spin lines, surfaces, and nodes in order to create surfaces or solids.
Use the Midlines tool to create midlines from existing lines, surface edges, or tube solids.
Extract the midsurface of thin solids, and review and edit midsurface plates.
Explore the tools used to edit geometry.
Clean up problematic areas on geometry.
FE geometry is topology on top of mesh, meaning CAD and mesh exist as a single entity. The purpose of FE geometry is to add vertices, edges, surfaces, and solids on FE models which have no CAD geometry.
Different types of mesh you can create in HyperWorks.
Create and edit 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D elements.
Create, organize and manage parts and subsystems.
HyperMesh composites modeling.
Create connections between parts of your model.
Rapidly change the shape of the FE mesh without severely sacrificing the mesh quality.
Create a reduced ordered model to facilitate optimization at the concept phase.
Workflow to support topology optimization model build and setup.
Multi-disciplinary design exploration and optimization tools.
Validate the model built before running solver analysis.
Tools used for crash and safety analysis.
Airbag solutions offer airbag folder utilities and exports a resulting airbag in a Radioss deck.
Essential utility tools developed using HyperWorks-Tcl.
Import an aeroelastic finite element model with Nastran Bulk Data format.
Framework to plug certification methods to assess margin of safety from the model and result information.
Streamline the creation of properties and 1D stiffener mesh using the info read from Marine CAD tools.
Create evaluation lines, evaluate them, and optimize the interfaces to eliminate squeak and rattle issues.
Explore the GeoD user interface.
Panels contains pre-processing and post-processing tools.
Results data can be post-processed using both HyperMesh and HyperView.
HyperGraph is a data analysis and plotting tool with interfaces to many file formats.
MotionView is a general pre-processor for Multibody Dynamics.
MediaView plays video files, displays static images, tracks objects, and measures distances.
TableView creates an Excel-like spreadsheet in HyperWorks.
TextView math scripts reference vector data from HyperGraph windows to automate data processing and data summary.
Create, define, and export reports.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
Explore the tools used to create geometry.
A surface represents the geometry associated with a physical part. A surface is a two-dimensional geometric entity that may be used in automatic mesh generation.
Use the Surfaces: Cross Extend tool to extend surfaces to meet each other, or other target surfaces.
Use the Surfaces: Cross Extend tool to extend surfaces to meet each other, or other target surfaces.

 to define cross extension
options.
to define cross extension
options.
© 2022 Altair Engineering, Inc. All Rights Reserved.