Translate Panel
Use the Translate panel to move entities in a single specified direction.
Location: Tool page
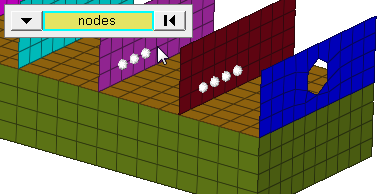
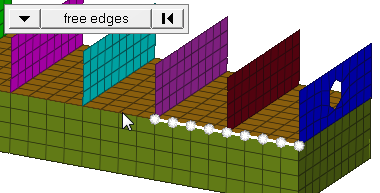
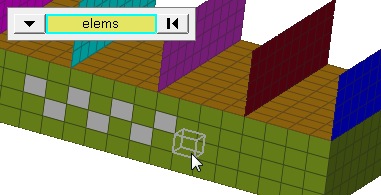
Figure 1. Elements Selected, Highlighted
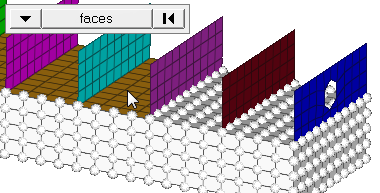
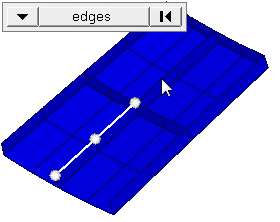
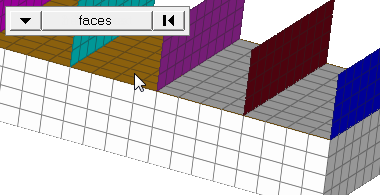
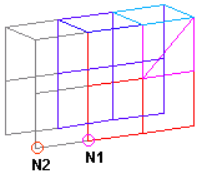 Figure 2. Elements Before Translation. The translation will occur in the direction from N1 to N2. |
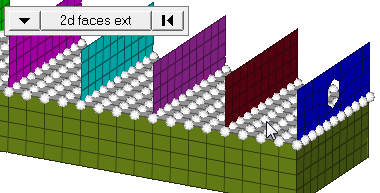
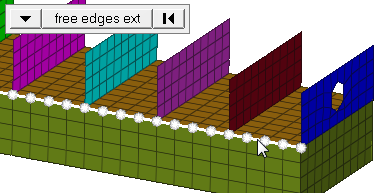
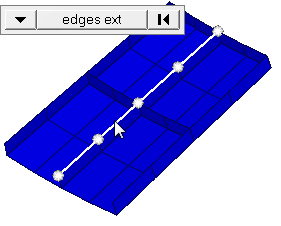
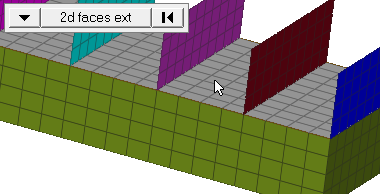
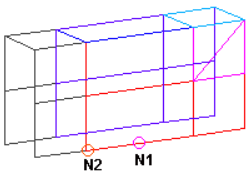 Figure 3. Elements After Translation. The selected elements have moved in the direction of N1 to N2. |
Common Errors
- N3 should not be selected for a direct move from N1 to N2.
When using the magnitude = N2-N1 option, you cannot use N3 to define the direction of translation; the direction is wholly defined by N1 and N2.
- N1 N2 N3 and vector options do not utilize local coordinate system
information.
When using either one of these options for the plane selector, set the coordinate system to global system.
Panel Options
| Option | Action |
|---|---|
| entity selector | Select entities for
translation. When you select nodes or elems, click the
switch to change the selection mode.
|
| coordinate system | Choose a coordinate
system type.
|
| direction selector | Select the direction in which selected entities will be moved. |
| magnitude = | Choose between a
specified number of units or a derived one.
|
| scale= | Specify a value to
scale the vector between the N1 and N2 nodes. The value you
specify must be between 0.1 and 10. By default, the scale value
is 1. Note: Available when magnitude= N2-N1.
|
| face angle / individual selection |
|
| edge angle |
Split edges that belong to a given face. When the edge
angle is 180 degrees, edges are the continuous boundaries of faces. For smaller
values, these same boundary edges are split wherever the angle between segments
exceeds the specified value. A segment is the edge of a single element.
Important: Only available when the entity selector is set to nodes and the
selection mode is set to free edges, free edges ext, edges, or edges
ext.
|
Command Buttons
- Undo by translating in the opposite direction without changing any of the input data (for example use the same direction and magnitude settings).
- When translating components, all of the geometry (points, lines, surfaces, and connectors) and elements (nodes) contained in the component are automatically translated.
- Translating nodes or elements does not change connectivity or continuity of a mesh.
- Translating only some of the nodes of an element may result in distortion of the element.
- Translating surfaces may affect edge topology, that is, shared edges becoming free edges.
- Translating elements or surfaces independently breaks any associations between the surfaces and the elements (nodes) created on them. Using reject will restore the associations if only one translation has been made, but translating in the opposite direction (as described above for "undoing" a translation) will not do so. Lost associations can also be restored via the Node Edit panel.
- Translating realized connectors will not unrealize them or translate the associated elements.
- When using spherical or cylindrical local coordinate systems, the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis buttons in the plane selector don't change. In such cases, the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis options correspond to the first, second, and third axes of such systems.
| Button | Action |
|---|---|
| translate + | Translate the selection in the positive
direction. For example, when translating nodes along the x-axis
this would move each selected node to a higher X coordinate
value. Note: If the magnitude is negative this
actually moves the coordinates to lower X
values.
|
| translate - | Translate the selection in a negative direction. For example, a node at X,Y,Z coordinates (50,33,42) translated along the global x-axis with a magnitude of 5 would move to (45,33,42). |
| reject | Revert the last translation. Only the most recent translation can be rejected; to undo multiple translations, simply translate in the opposite direction. Each positive translation can be undone by a negative translation of the same magnitude and direction. |
| return | Complete the translation and exit the Translate
panel. Note: This also clears your
selections.
|