Remove Preserved Nodes
Use the Preserve Node panel to remove preserved nodes from your model.
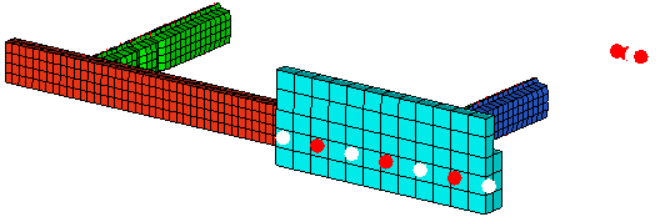
Figure 1. Preserve Nodes Selected. Selected nodes are highlighted white.
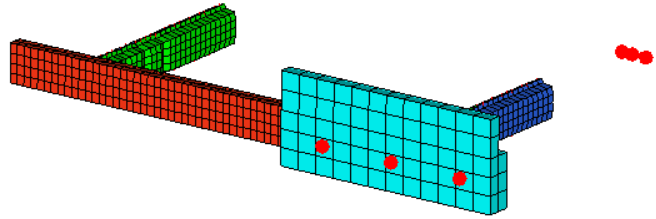
Figure 2. Preserve Nodes Removed
View new features for HyperWorks 2022.
Learn the basics and discover the workspace.
Discover HyperWorks functionality with interactive tutorials.
Start HyperWorks and configure the applications.
Create, open, import, and save models.
Set up sessions and create report templates.
Solver interfaces supported in HyperWorks.
A solver interface is made up of a template and a FE-input reader.
Create and edit 2D parametric sketch geometry.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
FE geometry is topology on top of mesh, meaning CAD and mesh exist as a single entity. The purpose of FE geometry is to add vertices, edges, surfaces, and solids on FE models which have no CAD geometry.
Different types of mesh you can create in HyperWorks.
Create and edit 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D elements.
Create, organize and manage parts and subsystems.
HyperMesh composites modeling.
Create connections between parts of your model.
Rapidly change the shape of the FE mesh without severely sacrificing the mesh quality.
Create a reduced ordered model to facilitate optimization at the concept phase.
Workflow to support topology optimization model build and setup.
Multi-disciplinary design exploration and optimization tools.
Validate the model built before running solver analysis.
Tools used for crash and safety analysis.
Airbag solutions offer airbag folder utilities and exports a resulting airbag in a Radioss deck.
Essential utility tools developed using HyperWorks-Tcl.
Import an aeroelastic finite element model with Nastran Bulk Data format.
Framework to plug certification methods to assess margin of safety from the model and result information.
Streamline the creation of properties and 1D stiffener mesh using the info read from Marine CAD tools.
Create evaluation lines, evaluate them, and optimize the interfaces to eliminate squeak and rattle issues.
Explore the GeoD user interface.
Panels contains pre-processing and post-processing tools.
Use the Accels (accelerations) panel to create and update concentrated accelerations by applying a load, representing accelerations, nodes, components, sets, surfaces, points, or lines.
Use the Acoustic Cavity Mesh panel to create a fluid volume mesh for the open-air volumes of an enclosed compartment, such as the passenger compartment of a vehicle. Structural components such as seats are modeled as separate acoustic volumes. Once generated, this mesh can be used in noise/vibration testing.
Use the Admas panel to create and update masses applied to nodes. The Adams panel supports the /ADMAS Radioss and *ELEMENT_MASS LS-DYNA element.
Use the ALE Setup panel to create and modify input data pertaining to the Arbitrary-Lagrangian-Eulerian.
Use the Animation Secondary panel to control the display of your model during animation sequences.
Use the Apply Result panel to apply the result's analysis data to selected entities of your model, or create loads from the analysis data.
Use the Assemblies panel to create and modify assemblies, which are collections of component and multibody collectors or other assemblies. This method of grouping component and multibody collectors is useful because once an assembly is created, it is possible to display components or multibodies by assembly, or to select entities by assembly rather than by component.
Use the Autocleanup panel to perform automatic geometry cleanup and prepare your model for meshing based on the parameters set in the BatchMesher criteria file.
Use the Automesh panel to generate a mesh of plate elements using surface geometry or existing shell elements to define the mesh area.
Use the Automeshing Secondary panel to create meshes interactively on surfaces, or create meshes without a surface present.
Use the Axis Labels panel to edit the axis label information of the current plot or selected attributes in a group of plots.
Use the Axis Scaling panel to modify plot axes.
Use the Bars panel to create, review, or update bar2 or bar3 elements.
Use the Beamsection Collectors panel to create and update beamsection collectors.
Use the Blocks panel to create and modify a block entity, which are commonly used in most crash solvers.
Use the Bodies panel to create, review, and update group entities.
Use the Border panel to edit the appearance of the border that designates the window around an xy plot.
Use the By Width option in the Extended Entity Selection menu to select surfaces based on their width.
Use the By Window option in the Extended Entity Selection menu to create a window that can be used to select entities on your model.
Use the Card Editor panel to select entities whose card image you want to view or edit.
Use the Card Image panel to edit solver specific data on a set of entities.
Use the CFD Tetramesh panel to generate hybrid grids, containing hexa/penta/tetra elements in the boundary layer and tetra elements in the core or fare field.
Use the Check Elems pane to verify the basic quality of your elements, as well as the geometric qualities of those elements.
Use the Color panel to change the color attributes of a collector.
Use the Component collectors panel to create and update components.
Use the Composite Shuffle panel to define manufacturing constraints for composite shuffling optimization.
Use the Composite Size panel to define manufacturing constraints for composite sizing optimization.
Use the Composites panel to assign and review the element material orientation of a mesh of shell and continuum shell elements, or to review the fiber direction (ply angle) of individual composite layers.
Use the Cones panel to create an analytic, conical or cylindrical surface and/or mesh.
Use the Config Edit panel to make changes to the configuration of existing elements.
The Connectors module contains several connector-specific panels that can be used to create and manage connectors.
Use the Constr Screen panel to define the data for constraint screening.
Use the Constraints panel to place constraints or enforced displacements on a model. This is accomplished by assigning a degree of freedom (DOF) constraint to the node.
Use the Contactsurfs panel to create and modify contactsurf entities.
Use the Contour Loads utility to create contour plots of applied loads and boundary conditions contained within load collectors.
Use the Contour panel to create contour and assigned plots of your model, and view your analysis results, in either a contour or assigned plot mode.
Use the Control Cards panel to set job-level, solver specific data.
Use the Control Vol panel to define control volume objects within a model.
Use the Convert panel to exchange data between different solver formats.
Use the Count panel to obtain a count of all the entities in your database.
Use the Curve Attributes panel to create and edit curves displayed on an xy plot.
Use the Dconstraints panel to create constraints for an optimization problem.
Use the Defeature panel to find and delete pinholes, fillets on surfaces and surface edges, and duplicate surfaces.
Use the Deformed (deformed shape) panel to plot displacement analysis results.
Use the Delete panel to delete data from a model database, preview and delete empty collectors, and preview and delete unused property collectors, material collectors, or curves. You can also delete an entire model database, if you wish to start with a clean database.
Use the Dependency panel to find nodes that have their degrees of freedom removed by a constraint or MPC (multiple point constraint) more than once. By identifying and correcting such dependencies prior to solving, solution errors can be avoided.
Use the Dequations panel to create user-defined functions for responses and design properties.
Use the Desvar Link panel to link a design variable to other design variables.
Use the Detach panel to detach elements from the surrounding structure. You can detach elements from a portion of your model so that it can be translated or moved, or you can offset the new nodes by a specified value. You can also use this panel to detach and remove elements from your model.
Use the Dimensioning panel to create and manipulate dimension features.
Use the Discrete dvs panel to define a discrete design variable value table for use in size or shape optimization, which maybe be referenced in the ddval = field on the Size, Gauge or Shape panels..
Use the Distance panel to determine the distance between two nodes/points or the angle between three nodes/points, or to change distances or angles.
Use the Drag panel to create a surface and/or mesh by dragging a series of nodes or lines, or to create elements by dragging selected elements. The selected entities are dragged along the specified vector creating a mesh, surface, or elements along that vector.
Use the Dummy Positioning / Joint dof panel to rotate the dummy assemblies or specify the position of the H-Point of a dummy assembly. The dummy database must be organized as a tree structure.
Use the Edge Edit panel to alter the connectivity status (topology) of adjacent surface edges, and stitch or split surfaces, replace fillets with corners, and suppress or eliminate redundant edges.
Use the Edges panel to find the free edges in a group of shell elements, find "T" connections in a group of shell elements (any edges connected to three or more elements), display duplicate nodes, and equivalence duplicate nodes.
Use the Edit Curves panel to create new curves or edit existing ones.
Use the Edit Element panel to hand build, combine, split, or modify elements.
Use the Elem Offset panel to create and modify elements by offsetting from a mesh of plate or shell elements.
Use the Elem Types panel to select the type of element to create, and also allows you to change existing element types.
Use the Element Cleanup panel to perform automatic cleanup of 2D elements based on the element quality criteria from the Quality Index panel or a separate criteria file.
Use the Ellipsoids panel to create and modify a single or multiple ellipsoids and cylinders.
Use the Entity Sets panel to create, update, and review named sets of entities.
Use the Equations panel to create, review, and update equations.
Use the Faces panel to find the free faces in a group of elements, and operates in the same manner as edges, but in 3D. It also allows you to find and delete duplicate nodes.
The fatigue configuration file is a user-defined external ASCII-file through which the data groups from results of static/modal/transient analysis of different solvers can be read.
Use the Fatigue panel to write stress, strain, force, and moment results from finite element analysis to an external file that can then be used to set up fatigue analysis.
Use the FE joints panel to create, review, or update joint elements. A joint element is a definition of a connection between two rigid bodies. Joint elements store a property and orientation information.
Use the Features panel to identify geometric features of a finite element model based on the relative angle between adjacent elements.
Use the Find panel to locate entities in a database.
Use the Finite Difference panel to access the finite difference panels.
Use the Flux panel to apply concentrated fluxes to your model. This is accomplished by applying a load, representing fluxes, to element nodes. Fluxes are load config 6 and are displayed as a thick arrow labeled with the word "flux."
Use the Forces panel to create concentrated forces. This is accomplished by applying a load, representing forces, to a node, point, set, or component.
Use the Free Shape panel to define design domains for free shape optimization.
Use the Free Size panel to define design domains for free size optimization.
Use the Gaps panel to create gap elements.
Use the Gaps panel to create gap elements. When using the OptiStruct solver interface, it allows the creation of multiple node-element gap elements.
Use the Gauge panel to create design variables (DESVAR) and property relation (DVPREL1) cards for shell and composite laminate components (PSHELL, PCOMP, and PCOMPG) selected for size optimization.
Use the Global panel to control global parameters that are accessed by several different panels. These parameters remain constant until changed. It also controls which components or collectors are active. Any entities you create are stored in the active collectors. Finally, you can use this panel to specify which template file you want to use. (Template files must first be created.)
Use the Grid Attributes panel to edit the grid line information contained in a plot.
Use the Grid Labels panel to edit the grid labels on the x and y axes of a plot. It allows you to change the font and color of the grid tic marks.
Use the Hidden Line panel to create hidden line plots of the displayed structure.
Use the HyperBeam panel to create beam cross-section entities that you can use to simplify complex portions of your model into simple bar elements.
Use the HyperMorph module to alter models in useful, logical, and intuitive ways while keeping mesh distortion to a minimum.
Use the Integrate panel to obtain the area under a curve. The area under the curve that has been integrated is shaded and the total area, based on the calculation, is given.
Use the Interfaces panel to create and modify interfaces. Interfaces are mainly used to define contact interactions between various parts of the model.
Use the Joints panel to create, review and update joint elements for use in an OptiStruct Multi-Body Dynamics simulation.
Legends display the range of values for the plot. Use the Legend Edit panel to change the number of colors in the legend or the colors of the legend. You can also reverse the colors used in the legend.
Use the Legend (xy legend) panel to edit the legend associated with an xy plot, for example you can change the font size or the location of the legend.
Use the Length panel to determine the length of a selected group of lines, and determine the length of the black line.
Use the Line Drag panel to create a two- or three-dimensional surface and/or mesh or elements by dragging nodes, lines, or elements along another line.
Use the Line Edit panel to split, join, or extend lines.
Use the Line Mesh panel to create a chain of one-dimensional elements such as beams along a line.
Use the Linear 1D panel to create one-dimensional elements.
Use the Linear Solid panel to create solid elements between two groups of plate elements.
Use the Lines panel to create lines using a wide variety of methods.
Use the Load Collectors panel to create and organize load collectors in your model.
Use the Load on Geom panel to map loads or boundary conditions from geometrical entities (loads on geometry) to the associated FE mesh entities (loads on mesh).
Use the Load Steps panel to create and update collections of load collectors, groups, and output blocks.
Use the Load Types panel to update load types and equations.
Use the Loads Summary tool to create a summary of the loads (node-based forces or moments, and element-based pressures) applied to a model
Use the Loadsteps panel to create Nastran and OptiStruct loadstep entities, which directly correspond to Nastran and OptiStruct loadstep definitions..
Use the Markers panel to create, review and update sensor entities.
Use the Mask panel to mask entities from the display list.
Use the Mass Calc panel to obtain the mass, area, and/or volume of a selected group of elements, solids, or surfaces.
Use the Masses panel to create mass elements.
Use the Material Collectors panel to create, review and edit collectors and card card images or dictionaries.
Use the MBS joints panel to define kinematic joints between two local coordinate systems to connect two multibody collectors. The HyperWorks entity created is an mbjoint.
Use the MBS planes panel to create rectangular, planar surfaces for use in multi-body analyses. The created entity is an mbplane.
Use the Mesh Edit panel to extend a mesh to meet another mesh and form a good connection between them, or to imprint overlapping meshes so that they match one another.
Use the Midmesh Panel to automatically generate a mesh at the midplane location, directly from the input geometry (components, elements, solids or surfaces), without first creating a midsurface.
Use the Midsurface panel to extract the midsurface representation of a solid part or to generate a finite element shell representation of a solid geometry.
Use the Moments panel to create concentrated moments by applying a load, representing moments, to a node.
Use the Multibody Collectors panel to generate new multibody collectors.
Use the Node Edit panel to associate nodes to a point, line, or surface/solid face; move nodes along a surface; place a node at a point on a surface; remap a list of nodes to a line; or project nodes to an imaginary line passing through two nodes.
Use the Nodes panel to create nodes using a wide variety of methods.
Use the Normals panel to display and reverse the normals of elements or surfaces. The orientation of element normals can also be adjusted. The normal of an element is determined by following the order of nodes of the element using the right-hand rule.
Use the NSM panel to add non-structural mass entities to a model, or modify existing ones.
Use the Numbers panel to display the IDs of an entity.
Use the OBJ Reference panel to define a response and its reference values for a minmax (maxmin) optimization problem.
Use the Objective panel to define the objective function for an optimization problem.
Use the On Plane panel to select entities that are on or touch a plane.
Use the Opti Control panel to define control parameters for an optimization.
Use the Optimization panel to access the most frequently used topology, topography, size, and shape optimizations panels.
Use the Options panel to modify default settings in HyperWorks.
Use the OptiStruct panel to execute an OptiStruct run on your desktop.
Use the Order Change panel to change element order.
Use the Organize panel to (re)organize your database by copying or moving data (entities) among collectors, includes, or parts.
Use the Ossmooth panel to extract and import the final design geometry from OptiStruct's topology, topography and shape optimization results into HyperWorks.
Use the Output Blocks panel to create and update blocks of entities used for output requests.
Use the Penetration panel to check for penetrations and/or intersections of elements. After running the check, you can use additional tools to check the penetration depth and move nodes in order to fix the problem areas; both penetrations and intersections can be fixed.
Use the Permute panel to switch coordinates of model entities in the global coordinate system.
Use the Perturbations panel to setup shape optimization.
Use the Planes panel to create a square, planar surface and/or mesh in a user-specified plane, or a surface and/or mesh bounded by planar lines.
Use the Plot Titles panel to edit the title information contained in a plot.
Use the Plots panel to create and manage plot collectors.
Use the Point Edit panel to perform many point-specific geometry cleanup tasks.
Use the Points panel to create free points using a wide variety of methods.
Use the Position panel to specify a new position for model entities.
Use the Preserve Node panel to review free, temporary, and preserved nodes, convert free and temporary nodes into preserved nodes, convert free and temporary nodes into preserved nodes, and remove preserved nodes.
Use the Preserve Node Panel to review the preserved and temporary nodes in your model.
Use the Preserve Node panel to convert free and temporary nodes into preserved nodes, which will be permanently saved in your model or a Solver deck.
Use the Preserve Node panel to convert free and preserved nodes into temporary nodes, which will only be saved as long as they are marked as a temporary node.
Use the Preserve Node panel to remove preserved nodes from your model.
Use the Pressures panel to create pressure loads on elements by applying a load, representing pressures, to a 1D or 2D element, or to the face of a solid element.
Use the Project panel to project data entities to a plane, vector, surface, or line.
Use the Property Collectors panel to create property collectors, which are used to assign physical properties to entities.
Use the Quality Index panel to calculate a single value to represent the quality of the displayed shell (2D) model.
Use the Quality Index Cleanup Tools secondary panel to access tools that assist you in manually relocating nodes and optimizing element topology.
Use the Query Curves panel to determine the x and y values of points in a curve on a plot.
Use the Quick Edit panel to split surfaces and washers, change the category (shared, free, and so on) of edges, create or delete surfaces and points, project points, and trim fillets.
Use the Radioss panel to execute a Radioss run on your desktop from HyperMesh.
Use the RBE3 panel to create, review, and update RBE3 elements.
Use the Read Curves panel to read in an xy data set from an ASCII file. As a result, an xy curve is created that represents that data graphically.
Use the Rebuild Mesh panel to streamline the process of remeshing existing meshes to generate a new mesh with good quality and flow.
Use the Reflect panel to reflect portions of a model about a plane, changing the selected portion into a mirror image of itself.
Use the Rename panel to change the name of a specific collector or to rename types of collectors to their respective ID with an optional prefix.
Use the Renumber panel to renumber entities. You may also enter a value by which to offset the IDs of entities.
Use the Reorder panel to change the order of named entities in database.
Use the Replace panel to relocate one node to the position of another or manually equivalence two nodes.
Use the Responses panel to create responses for an optimization.
Use the Results Curves panel to create curves by extracting data from an HyperWorks binary results file.
Use the Ribs panel to create and modify simple ribs between two surfaces.
Use the Rigid Walls panel to create and update rigid walls.
Use the Rigids panel to create rigid or rigid link elements.
Use the Rods panel to create rod elements.
Use the Rotate panel to rotate entities around an axis in space.
Use the Ruled panel to create surfaces and/or meshes of plate elements from nodes, lines, and/or line segments, in any combination.
Use the Safety module to access the panels most frequently used in safety analysis.
Use the Scale panel to increase or decrease an entity's dimensions.
Use the Sensors panel to create and edit modify sensors.
Use the Shape panel to create shape design variables and associate them to a shape for shape optimization.
Use the Shrink Wrap panel to generate an enclosed volume or solid mesh, and is typically used to approximate and simplify an existing model.
Use the Simple Math panel to access tool for applying mathematical operations to curves.
Use the Size panel to define design variables and properties for size optimization.
Use the Skin panel to create a skin surface and/or mesh from a set of lines.
Use the Smooth panel to improve element quality in a surface-based mesh or a mesh of solid elements using one or more algorithms that adjust node positions to moderate sharp variations in size or quality in adjacent elements.
Use the Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics panel to perform SPH analysis on a component with volume, such as airbags or fuel tanks.
Use the Solid Edit panel to modify solid entities.
Use the Solid Map panel to create a mesh of solid elements in a solid geometric volume.
Use the Solid Mesh panel to create meshes in a pentagonal or hexagonal volume defined with edge lines.
Use the Solids panel to create solid geometry using a wide variety of methods.
Use the Solver panel to run an external program from within HyperWorks or assign and run a solver on selected analysis decks.
Use the Spheres panel to create a spherical surface and/or mesh.
Use the Spherical Clipping panel to focus on specific areas of the model by displaying only the portions of a model inside a three-dimensional spherical volume, while masking everything outside the sphere.
Use the Spin panel to create a surface and/or mesh or elements by spinning a series of nodes, a line or lines, or a group of elements about a vector to create a circular structure.
Use the Spline panel to create a shell mesh and/or surface. A mesh and surface can be created using nodes, points, or lines. You can also use the Spline panel to create a mesh without a surface, or a surface without a mesh.
Use the Split panel to split plates or solid elements. In addition, hexa elements can also be split using a technique that moves progressively through a row of elements in the model.
Use the Spotweld panel to create 1D elements to connect different parts.
Use the Springs panel to create spring elements.
Use the Summary panel to obtain a summary of component element counts or element properties of the current model.
Use the Super Elems panel to assign nodes to a super element set. You can also display the nodes that belong to a super element.
Use the Surface Edit panel to perform a variety of surface editing, trimming, and creation functions. This panel also allows you to offset surfaces in their normal direction.
Use the Surface Transparency panel to set the transparency level for the surfaces of selected components.
Use the Surfaces panel to create surfaces using a wide variety of methods.
Use the Systems Collectors panel to create and update system collectors.
Use the Systems panel to create rectangular, cylindrical and spherical coordinate systems. Use this function when you want to define nodes, loads and constraints in a different coordinate system.
Use the Table Entries panel to specify table entries for use in equations for responses and design properties.
Use the Tags panel to assign names to nodes, elements, lines, surfaces, points, and solids. An entity name is then used to reference the entity across multiple versions of the same model.
Use the Temp Nodes panel to control which nodes are on the temporary node mark.
Use the Temperatures panel to create temperature constraints.
Use the Tetramesh panel to fill an enclosed volume with first or second order tetrahedral elements.
Use the Titles panel to create, edit, and move screen titles and entity tags.
Use the Topography panel to define design domains for topography optimization.
Use the Topology panel to define design domains for topology optimization.
Use the Torus panel to create an analytic, toroidal surface and/or mesh.
Use the Transient panel to create an animation sequence from transient results.
Use the Translate panel to move entities in a single specified direction.
Use the True View panel to change the current view of your model based on a model vector or angles.
Use the Vectors Collectors panel to create and update vector collectors.
Use the Vector Plot panel to create analysis-based vector plots.
Use the Vectors panel to create a vector entity.
Use the Velocities panel to create concentrated velocities.
Use the Window panel to control xy plot window size and placement.
Use the XY Plots panel to access the XY Plotting panels.
Results data can be post-processed using both HyperMesh and HyperView.
HyperGraph is a data analysis and plotting tool with interfaces to many file formats.
MotionView is a general pre-processor for Multibody Dynamics.
MediaView plays video files, displays static images, tracks objects, and measures distances.
TableView creates an Excel-like spreadsheet in HyperWorks.
TextView math scripts reference vector data from HyperGraph windows to automate data processing and data summary.
Create, define, and export reports.
Panels contains pre-processing and post-processing tools.
Use the Preserve Node panel to review free, temporary, and preserved nodes, convert free and temporary nodes into preserved nodes, convert free and temporary nodes into preserved nodes, and remove preserved nodes.
Use the Preserve Node panel to remove preserved nodes from your model.
Use the Preserve Node panel to remove preserved nodes from your model.


© 2022 Altair Engineering, Inc. All Rights Reserved.